Energy Systems
Use Batteries for Energy Storage
What Is It?
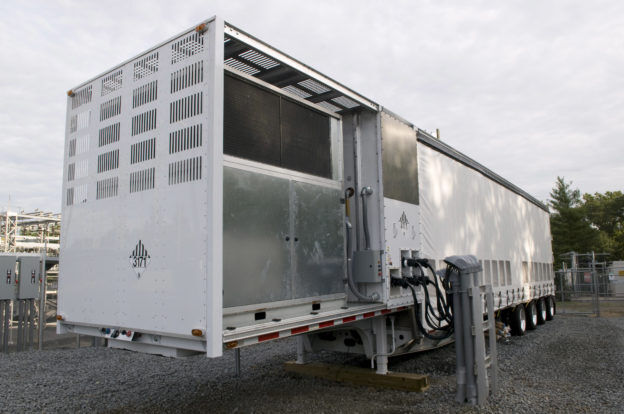

Batteries can be used to store energy for emergencies or to shift building energy usage to off-peak periods, which has the impact of lowering demand-based utility charges. Battery systems can be used in isolation, and are increasingly being used with solar photovoltaics (PV). With the introduction of more modular energy storage systems and declining prices, the use of batteries is becoming more common. Some existing buildings have lead-acid batteries to mitigate service interruptions. Ionic battery pack systems are significantly safer than lead-acid battery banks, represent a lower risk of toxic leaks and fire, and are more energy efficient.
Batteries are an easy retrofit for energy resilience. In the event of an emergency, they can be used to maintain power for essential functions for hours or days. Battery storage can be a more economical way to provide backup power as they can reduce energy bills outside of emergencies. They are also not reliant on delivered fuel.
Benefits
- Retains energy for emergencies, and could be used in place of a fuel-powered generator
- Could enable a building to island from the grid in the case of an emergency
- Prevents service interruptions in the event of a power outage
- May save money by demand shaving in locations with variable energy rates. During peak hours where electricity prices are increased, the building can switch to battery power stored during cheaper off-peak hours
Drawbacks
- High initial costs
- Lack of precedent in commercial and industrial applications
- Unlike generators, which can be refueled, batteries have a finite supply of power in the case of an emergency
- High-capacity batteries can be very large – some are sold in a shipping container
Regulatory Impacts and Requirements
Potential regulatory touchpoints in Boston and Massachusetts include:
- Fire Department
- Boston Public Works Department
Financing Options, Incentives, and Rebates
- Reduces the cost of high-demand charges by cutting down on the electricity purchased during peak hours.
- FEMA’s PDM Program is designed to assist in implementing a sustained pre-disaster natural hazard mitigation program. This program awards planning and project grants and provides opportunities for raising public awareness about reducing future losses before disaster strikes. PDM grants are funded annually by Congressional appropriations and are awarded on a nationally competitive basis.
- For grid-type storage:
- Accelerated Depreciation for SmartMeters and Smart Grid Systems: Reduces the cost-recovery period for smart systems from 20 years to 10 years.
- Community Clean Energy Resiliency Initiative – Massachusetts awards grants to municipalities that use technology and clean energy systems to prevent service interruptions.
NEWS
- “Battery storage: The next disruptive technology in the power sector,” McKinsey & Company, June 2017
- "Is Tesla's Powerwall Battery a Utility Killer?" GreenBiz.com, May 4, 2015
- “Tesla's huge new batteries will store power for Amazon, Target, and others,” TheVerge.com, May 1, 2015
RESOURCES
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Economic Analysis Case Studies of Battery Energy
- Rocky Mountain Institute: The Economics of Battery Energy Storage
- CleanTechnica: Tesla Powerwall & Powerpacks Per-kWh Lifetime Prices vs Aquion Energy, Eos Energy, & Imergy