Paving and Asphalt
Use a Plastic Grid in Paving
What Is It?
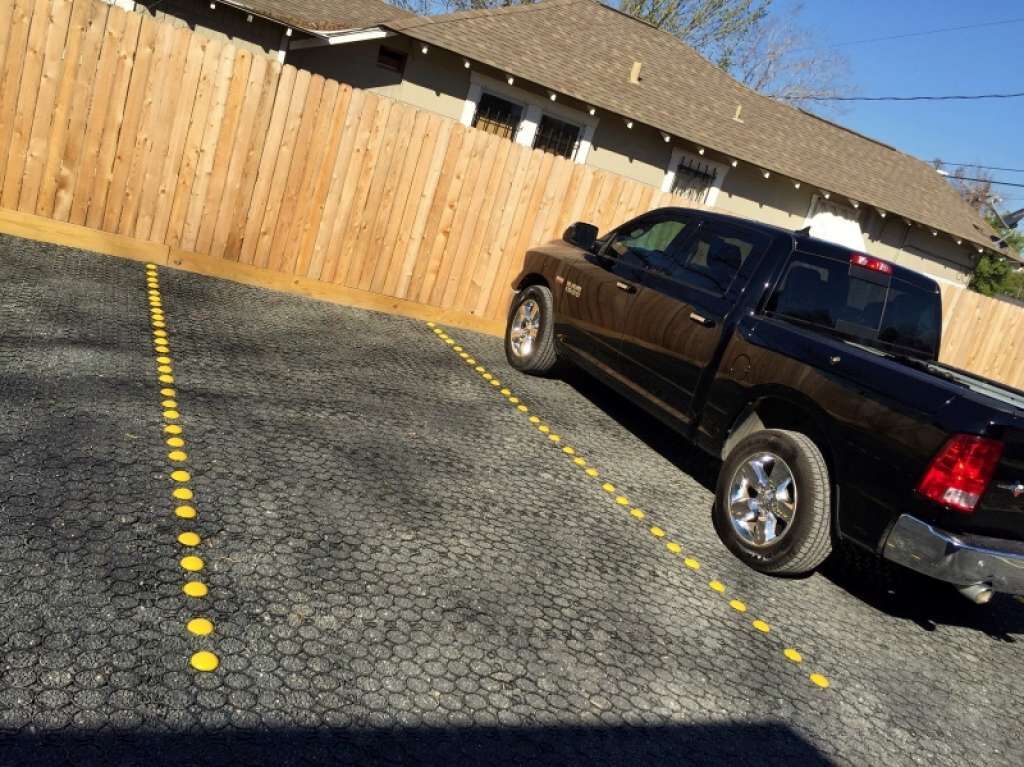

Houston Chronicle
Plastic grids are an alternative pavement, consisting of a durable interlocking plastic grid filled with gravel, earth, or seeded with grass. The grid is very porous, allowing for high rates of infiltration (up to 3 ft/hr), and the modular plastic cells can reduce erosion and wear on gravel and grass pathways. Due to the flexibility of the grid components, plastic grids can be used on sites with uneven terrain, though maximum slope ranges from 6 – 12% due to traction limitations.
Regular maintenance is typically low. Vegetated grids will need to be mowed and may need irrigation and occasional reseeding, while non-vegetated grids may need to be refilled with gravel or crushed rock. Vacuuming may be necessary to maintain high permeability. Plastic grids can be easily added onto existing paving, though care should be taken to ensure that high volumes of runoff are not directly routed from adjacent impervious areas onto the grid, as sediment can quickly clog the void spaces. Plastic grids are often made from recycled materials. Load bearing capacities range from 24,000 lb/sq ft. to 823,680 lbs/sq ft.
Benefits
- Enhances groundwater infiltration while reducing stormwater runoff volume, rate, and pollutants. Additional drainage facilities are not required
- Vegetated grids can lower urban air temperatures when moist due to evaporative cooling
- Quick installation time
- Reduces occurrence of black ice/freezing puddles in cold climates; lowers need for chemical deicers
Drawbacks
- Pollutants and deicing salts can infiltrate groundwater—should not be installed in areas where hazardous material spills are possible
- Poorly placed grids can become clogged due to excess runoff from impervious areas
- Load bearing strength and durability generally lower than permeable pavers/asphalt/concrete
- Vegetated pavers require regular maintenance and may require additional irrigation daytime
Regulatory Impacts and Requirements
Potential regulatory touchpoints in Boston and Massachusetts include:
- Boston Groundwater Trust
- Boston Water and Sewer Commission
- Local Utilities
- Boston Public Works Department
- Public Improvement Commission
- Zoning Board of Appeals
- Architectural Access Board
- MA Historical Commission/Boston Landmarks Commission
Financing Options, Incentives, and Rebates
- State of Massachusetts:
- Clean Water State Revolving Fund (SRF)
- Coastal Pollutant Remediation (CPR) Grant Program
- Section 319 Nonpoint Source Competitive Grant (Funding provided under federal Clean Water Act)
- 604b Water Quality Management Planning Grant (Funding provided under federal Clean Water Act)
- Drinking Water Supply Protection Grant Program
- Newton, MA: Municipal stormwater abatement service fees
News
- TERRAM Porous Pavers Are Engineered to Provide a Permeable Pavement Surface for All Types of Traffic" Specification Online, May 2016
- “Pavement That Prevents Flooding,” Houston Chronicle, June 2015
Resources
- California Coastal Commission: Permeable Pavement
- US EPA: See pg. 8 of the Cooling Pavements Chapter of their Heat Island Compendium
- Seattle Right of Way Manual: Permeable Pavement Comparison Guide
- University of Maryland: Permeable Pavement Fact Sheet
A Sample of Providers
Project Examples:
- Whole Foods Market, Houston, TX, used TrueGrid permeable paving with plastic grid for their parking lot.